These big solar winds change our bodies, brains, the earth, and time.
GEOMAGNETIC STORM WATCH (G2): Earth’s magnetic field is about to receive a double blow. First, on Dec. 4th, a high-speed stream of solar wind flowing from a coronal hole will arrive. Then, on Dec. 5th, an off-target CME could deliver a glancing blow. Their combined effect is expected to cause G1 (Minor) to G2-class (Moderate) geomagnetic storms with photographic auroras at mid-latitudes. Aurora alerts: SMS Text
A HOLE IN THE SUN’S ATMOSPHERE: A huge hole has opened in the sun’s atmosphere, and it spewing a stream of solar wind directly toward Earth. NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory photographed the structure, which stretches almost 800,00 km along its long axis:
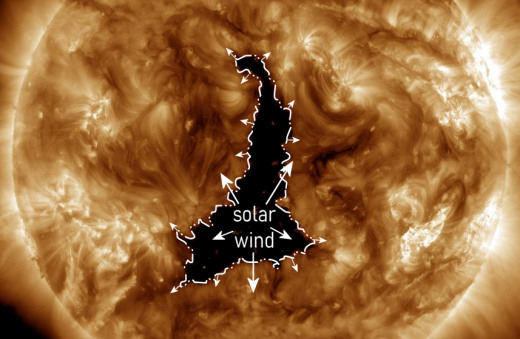
This is a coronal hole–a region in the sun’s atmosphere where magnetic fields have opened up, allowing solar wind to escape. The hole looks dark because hot glowing gas normally contained there is missing. The gaseous material is on its way to Earth.
The solar wind is due to arrive Dec. 4th or 5th. Together with a glancing-blow CME, also en route, it could spark G1 (Minor) to G2-class (Moderate) geomagnetic storms. Aurora alerts: SMS Text
| Cosmic Rays in the Atmosphere |
SPACE WEATHER BALLOON DATA: Almost once a week, Spaceweather.com and the students of Earth to Sky Calculus fly space weather balloons to the stratosphere over California. These balloons are equipped with sensors that detect secondary cosmic rays, a form of radiation from space that can penetrate all the way down to Earth’s surface. Our monitoring program has been underway without interruption for 7 years, resulting in a unique dataset of in situ atmospheric measurements.
Latest results (July 2022): Atmospheric radiation is decreasing in 2022. Our latest measurements in July 2022 registered a 6-year low:
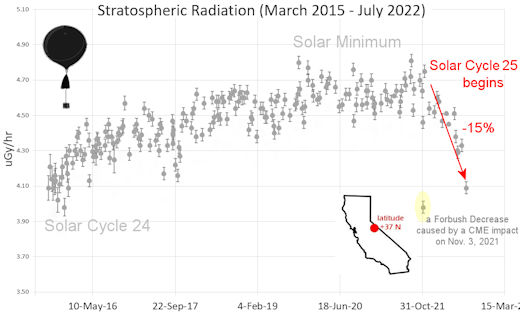
What’s going on? Ironically, the radiation drop is caused by increasing solar activity. Solar Cycle 25 has roared to life faster than forecasters expected. The sun’s strengthening and increasingly tangled magnetic field repels cosmic rays from deep space. In addition, solar coronal mass ejections (CMEs) sweep aside cosmic rays, causing sharp reductions called “Forbush Decreases.” The two effects blend together to bring daily radiation levels down.
Who cares? Cosmic rays are a surprisingly “down to Earth” form of space weather. They can alter the chemistry of the atmosphere, trigger lightning, and penetrate commercial airplanes. According to a study from the Harvard T.H. Chan school of public health, crews of aircraft have higher rates of cancer than the general population. The researchers listed cosmic rays, irregular sleep habits, and chemical contaminants as leading risk factors. A number of controversial studies (#1, #2, #3, #4) go even further, linking cosmic rays with cardiac arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death.
Technical notes: The radiation sensors onboard our helium balloons detect X-rays and gamma-rays in the energy range 10 keV to 20 MeV. These energies span the range of medical X-ray machines and airport security scanners.
Data points in the graph labeled “Stratospheric Radiation” correspond to the peak of the Regener-Pfotzer maximum, which lies about 67,000 feet above central California. When cosmic rays crash into Earth’s atmosphere, they produce a spray of secondary particles that is most intense at the entrance to the stratosphere. Physicists Eric Regener and Georg Pfotzer discovered the maximum using balloons in the 1930s and it is what we are measuring today.

